Environmental Health
Visit the LibraryOn emerging environmental health issues such as sanitation, waste management, and health risks, and policies surrounding essential environmental health services
Featured Publications

Environmental Health
POLICY BRIEF: From Research to Impact: Transformative Actions Against Arsenic Groundwater Contamination In Batangas
On the 12th of January 2020, Taal Volcano, located in Southwest Luzon in the Philippines, erupted greatly impacting the livelihood and health of the people in Batangas Province. With majority of Batangas province relying on the groundwater aquifer surrounding Taal Volcano, one of the world’s most active volcanoes globally, for drinking water, this volcanic event followed by continuous volcanic activity throughout 2020 prompted an investigation on the quality of groundwater sources in communities surrounding the volcano.
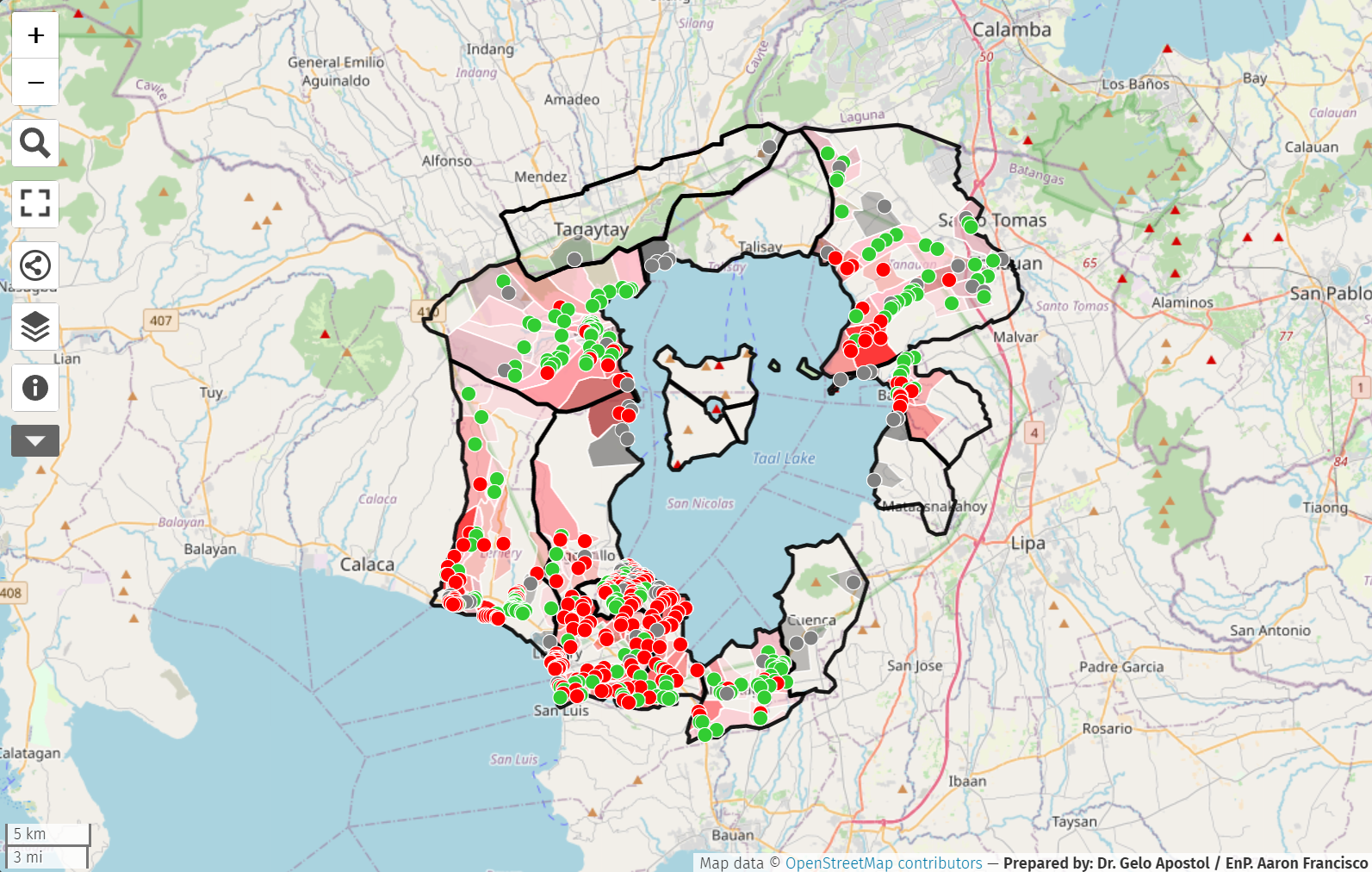
Environmental Health
A TAALe of Arsenic: Sharing the narrative through an interactive map
Arsenic is a highly toxic and carcinogenic trace metal that can potentially contaminate groundwater sources in volcanic regions and affect communities in the area, like those residing around the Taal Volcano. The volcano’s eruption last 2020 encouraged an investigation into the quality of groundwater sources in communities surrounding the volcano. In response, the EnviHealth team in ACRI conducted a comparative documentation, “Arsenic in Groundwater Sources from Selected Communities Surrounding Taal Volcano, Philippines”. Water samples from 26 wells were collected across 11 municipalities and 1 city in Batangas province within danger zones from the volcano which were used to analyze total arsenic levels of the samples. Geographic coordinates of the sampling points were also recorded for mapping.

Environmental Health
Policy Brief: Projecting Temperature-Related Dengue Burden in the Philippines Under Socioeconomic Pathway Scenarios
Dengue fever remains a major public health concern in the Philippines, with its transmission strongly influenced by temperature changes. The Environmental Health Flagship Team then conducted a study that explores the historical and projected dengue burden attributable to temperature variations under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathway (SSP) scenarios. The study highlights the need for robust policy measures to address this growing public health challenge, particularly in regions most affected by temperature-driven dengue transmission.

Environmental Health
Implementation Review of the Philippine National Action Plan (PNAP) to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) through One Health Approach 2019-2023 and the Development of a New Medium-Term AMR Action Plan for 2024-2028
ACRI together with the Department of Health (DOH), Department of Agriculture (DA), World Health Organization (WHO), and the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), played a central role in developing the Philippines’ 2024–2028 National Action Plan to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Building on the 2019–2023 plan, this new roadmap strengthens the country’s One Health approach—integrating human, animal, plant, environmental, and economic sectors—to curb the growing threat of AMR. With its research and technical expertise, ACRI contributed to ensuring that the plan is evidence-based, actionable, and sustainable, setting the direction for coordinated national efforts against one of the most urgent global health challenges.

Environmental Health
Advancing vaccine uptake to mitigate antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in low and middle-income countries of South or South-East Asia
This project explores how strengthening vaccine uptake can serve as a key strategy to mitigate antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the Philippines and across South and South-East Asia. By reducing the burden of vaccine-preventable diseases and the unnecessary use of antibiotics, the study aims to provide actionable recommendations for national and institutional stakeholders to better integrate vaccination initiatives into AMR control efforts, ultimately contributing to stronger, more resilient health systems.

Environmental Health
Incorporating Climate Change Strategies into AMR Intervention and Implementation Research Projects: A Scoping Review
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and climate change are two of today’s most pressing global health challenges, with rising temperatures and extreme weather events accelerating the spread of resistant microorganisms, particularly in vulnerable low- and middle-income countries. This project undertakes a scoping review to examine how climate change influences the development of AMR in livestock and aquaculture systems, while also assessing climate-smart practices, policies, and collaborative models that address both issues. Through literature synthesis, expert roundtables, and community dialogues, it seeks to generate evidence and insights that can inform integrated interventions, strengthen policy, and guide future research at the intersection of AMR and climate change.

Environmental Health
Understand and mitigating the influence of extreme weather events on HIV outcomes: A global investigation
The Philippines faces the dual crises of a rapidly expanding HIV epidemic and intensifying climate-related disasters, yet little is known about how extreme weather events affect HIV prevention, treatment, and care. This study addresses that gap by examining the impacts of typhoons, floods, and droughts on people living with HIV, with a focus on vulnerable populations such as men who have sex with men, transgender individuals, and people who inject drugs. The findings will provide vital evidence to inform climate-adaptive HIV care strategies and guide policies that protect at-risk communities during environmental crises.
More on Environmental Health
-
Environmental Health > Projects
Implementation Review of the Philippine National Action Plan (PNAP) to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) through One Health Approach 2019-2023 and the Development of a New Medium-Term AMR Action Plan for 2024-2028
ACRI together with the Department of Health (DOH), Department of Agriculture (DA), World Health Organization (WHO), and the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), played a central role in developing the Philippines’ 2024–2028 National Action Plan to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Building on the 2019–2023 plan, this new roadmap strengthens the country’s One Health approach—integrating human, animal, plant, environmental, and economic sectors—to curb the growing threat of AMR. With its research and technical expertise, ACRI contributed to ensuring that the plan is evidence-based, actionable, and sustainable, setting the direction for coordinated national efforts against one of the most urgent global health challenges.
Geminn Louis C. Apostol, MD, MBA, MSc, PhD (c), Sary Valenzuela, MD, Percival Ethan Lao, MD, Anna Beatrice Enriquez
-
Environmental Health > Projects
Incorporating Climate Change Strategies into AMR Intervention and Implementation Research Projects: A Scoping Review
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and climate change are two of today’s most pressing global health challenges, with rising temperatures and extreme weather events accelerating the spread of resistant microorganisms, particularly in vulnerable low- and middle-income countries. This project undertakes a scoping review to examine how climate change influences the development of AMR in livestock and aquaculture systems, while also assessing climate-smart practices, policies, and collaborative models that address both issues. Through literature synthesis, expert roundtables, and community dialogues, it seeks to generate evidence and insights that can inform integrated interventions, strengthen policy, and guide future research at the intersection of AMR and climate change.
Geminn Louis C. Apostol, MD, MBA, MSc, PhD (c), Percival Ethan Lao, MD, Hazel Ann Fajardo, MD, MPH
-
Environmental Health > Projects
Understand and mitigating the influence of extreme weather events on HIV outcomes: A global investigation
The Philippines faces the dual crises of a rapidly expanding HIV epidemic and intensifying climate-related disasters, yet little is known about how extreme weather events affect HIV prevention, treatment, and care. This study addresses that gap by examining the impacts of typhoons, floods, and droughts on people living with HIV, with a focus on vulnerable populations such as men who have sex with men, transgender individuals, and people who inject drugs. The findings will provide vital evidence to inform climate-adaptive HIV care strategies and guide policies that protect at-risk communities during environmental crises.
Geminn Louis C. Apostol, MD, MBA, MSc, PhD (c), Percival Ethan Lao, MD, Hazel Ann Fajardo, MD, MPH
-
Environmental Health > Projects
Advancing vaccine uptake to mitigate antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in low and middle-income countries of South or South-East Asia
This project explores how strengthening vaccine uptake can serve as a key strategy to mitigate antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the Philippines and across South and South-East Asia. By reducing the burden of vaccine-preventable diseases and the unnecessary use of antibiotics, the study aims to provide actionable recommendations for national and institutional stakeholders to better integrate vaccination initiatives into AMR control efforts, ultimately contributing to stronger, more resilient health systems.
Geminn Louis C. Apostol, MD, MBA, MSc, PhD (c), Hazel Ann Fajardo, MD, MPH, Percival Ethan Lao, MD
